David C. Eyre
Designed by Ronald Mason in Canada, the Christavia is produced in a number of models as a homebuilt aircraft and plans are available from the designer. Designed for work by missionaries in Africa, the name of the aircraft means Christ-in-Aviation.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Macro was a single-seat open-cockpit all-metal low wing monoplane designed by Alan Clarke and marketed by Elite Aircraft of Mulgrave, VIC in the 1980s.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
Elitar was formed in 1997 and commenced marketing a number of designs, including the IE-101, the IE 201 Senator, the IE 202 and the Sigma 4.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The CH-7 Angel was designed by Augusto Cicare in Argentina as a single-seat light cheap sporting helicopter powered by a 600-cc two-cycle two-cylinder dual-ignition liquid cooled engine. Aimed at a market for transport, tourism and agricultural use, the structure is of steel trestle weld and aluminium tubes bolted together,
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The ELA-10 Eclipse is one of a range of high-performance gyrocopters produced by ELA Aviacion of Cordoba in Spain and models include the ELA-7, ELA-8, ELA-9 Junior, and the top of the range Eclipse.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The ELA-09 Junior is one of arrange of gyroplanes designed and built in Spain for the gyrocopter market and has become popular around the world, having a wide speed range of 35-km/h (22 mph) to 120 km/h (74 mph) and a max speed of 150 km/h (93 mph).
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
ELA Aviacion in Spain commenced production of gyrocopters for the civil market in 1996 and by 2006 had becoming the largest ultralight manufacturer, and the only Spanish company to construction autogyros.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Topaz is one of a series of light aircraft developed in Poland for the light aircraft market, the Topaz being a development of the JK-05L Junior.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
Designed and built in Finland, the Pik-20 series of gliders emanated from a design by the University of Technology in Helsinki, design work commencing in 1971 and the first of two prototypes flew for the first time on 10 October 1973.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
Produced by Quicksilver Enterprises Inc of Temecula, California, the series commenced as an ultra-light aircraft, a powered variant of the Quicksilver hang-glider.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
In 1982 Walter Extra of Dinslaken, Germany, participated in the World Aerobatic Championships in a Pitts biplane and decided to build his own aircraft, setting up Extra Flugzugbau in 1983 and built the Extra 230, the first flight of which took place on 14 July 1983.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Extra 200 is a high-performance two-seat aircraft designed and marketed by Extra Flugzeugbau GmbH in Germany and aimed at the market for unlimited-category aerobatic aircraft.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Express was designed and developed by Wheeler Technology as a high-speed cross-country kitplane, with the unusual seating featuring one forward and one aft-facing seat in the rear, behind two side-by-side front seats with dual controls.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Express series was designed by Wheeler Technology Inc as a high-speed cross-country kitplane, and the prototype was built from kits of pre-moulded parts, the first aircraft flying on 28 July 1987.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
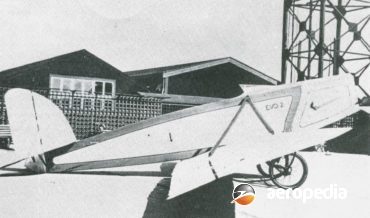
Brothers Arthur, Ronald and Ernest Everson built a small aircraft in about 1929, known as the Evo I, this being a simple high-wing glider-like design powered by a four-cylinder Henderson converted motor cycle engine, the aircraft being taken to the Mangere Speedway on 10 July 1929 but it crashed on
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
Evektor-Aerotechnic AS of Kunovice in the Czech Republic was formed in 1991 and a lot of its work over the years has been involved in the production of parts for aircraft designed by Aero Vodochy, particularly parts for military trainers.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Harmony is a sister aircraft to the Sportstar series (marketed in the United Kingdom as the Eurostar) and shares many of the design features of that type.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
After completion of the design of the single-seat VP-1, Mr Evans developed a two-seat variant, the VP-2.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Evans VP-1 and VP-2 series of light homebuilt aircraft was designed by Mr W S Evans in the USA with the idea of producing an aircraft which would be simple to build for the amateur constructor, and safe to fly with its all-wood construction.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Europa is an advanced composite homebuilt built from a kit and marketed by Europa Aviation Ltd in North Yorkshire, fitted with a retractable or fixed undercarriage.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Eurocopter EC-225 is a development of the former AS-332 Super Puma series to meet the requirements of oil companies to convey passengers, most being used in this area in the oil rig industry to convey workers to and from oil rigs around Australia.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The EC 175 is a multi-mission helicopter intended for the civil market which was developed by Eurocopter with the Harbin Aviation Industry Group in a joint venture.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The EC-145 is a development of the Bk-117 series. Work commenced on the design in 1997, the type being initially marketed in Japan as the Bk 117C-2.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The prototype of the EC-135 series (D-HECX) made its first flight at Ottobrunn, Germany on 5 February 1995, this being the first definitive aircraft following the completion of a test flying programme with two BO-108 technology demonstrators
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
In early 2001 at Heli-Expo Eurocopter announced a new helicopter had been added to its range, this being the EC-130 series based on the AS 350B3 but with a larger cabin and baggage area, and including the doors and windshield from the EC 120 Colibri series.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
One of a series of helicopters produced by Eurocopter, the Franco/German consortium. The prototype of the EC-120 Colibri (F-WWPA), initially designated the P120L, flew for the first time on 9 June 1995, the second prototype (F-WWPD) flying on 17 July 1996.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Ercoupe series of light two-seat monoplanes was designed to bring simplicity into flying.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Enstrom Corporation of Menominee County Airport, Michigan, was formed in 1959 by Rudy Enstrom to undertake the development and production of a small helicopter for private and commercial operation.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Model 480 was developed to increase mission flexibility and to provide a more affordable light turbine-powered helicopter to place on the market which for years was dominated by the Bell 206 and the Hughes 500.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Phenom 300 was developed by Embraer in Brazil with the advice of executives, pilots and owner/operators to meet the evolving needs of business travellers and has a ‘new Oval Lite profile’ with an interior designed by MBW Group Designworks USA to give a new level of comfort to
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
In 1939 the Douglas Aircraft Company decided to design and build a new four-engine airliner with an un-pressurised fuselage, providing accommodation for 42 passengers, and a range which was sufficient to permit US transcontinental performance, powered by the Pratt & Whitney R-2000 radial engine.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The DC-5 was designed by Ed Heineman (who later designed the A-4 Skyhawk) and built at the El Segundo Division of the Douglas Aircraft Co at Inglewood, California to meet airline requirements for a 16 – 22 seat twin-engine airliner.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The DC-6 series has been considered by many to be the finest piston-engined transport produced.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
In an attempt to maintain its competitive position as a supplier of transport aircraft to the world’s airlines, Douglas Aircraft Company commenced the design of a jet powered aircraft to replace the DC-7 series.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
In April 1963 the Douglas Aircraft Company proceeded with the design and development of a new airliner known as the Douglas Model 2086, at that time having no firm orders.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Dolphin was designed by the Douglas Aircraft Co to meet the requirements of civil operators for a twin-engine flying boat, and the prototype, initially known as the Sinbad, flew for the first time at Santa Monica Bay, California, in July 1930.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
This was a machine designed and built in Australia. It is a low-wing sporting monoplane developed in Queensland using the fuselage basically of the Foxcon Terrier 100, which has been developed and produced at Mackay and provided in kit form, lengthening it, making some other changes to meet the needs
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Skylark is one of the new light aircraft designed to meet US LSA requirements. It was designed in Canada and is manufactured in the Czech Republic.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Dragon Fly was designed in 1985 in Italy by two archeologists, Angelo and Alfredo Castiglioni, as a two-seat light helicopter to meet a requirement they had for a survey platform or research work.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Tundra is a STOL utility aircraft of all-metal construction, the constructor of the kit aircraft being based in Quebec, Canada.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
Recent Comments
Archives
Categories
- No categories
Categories
- No categories
Latest Posts
Newsletter