Photograph:
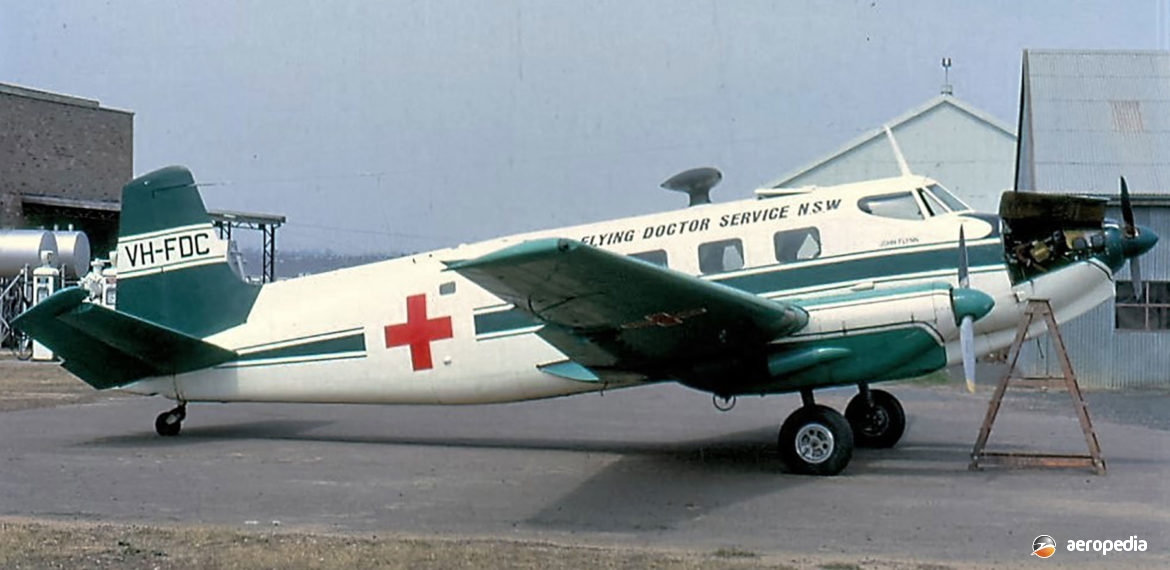
de Havilland DHA-3 Drover VH-FDC (c/n 5013) ‘John Flynn’ at Bankstown, NSW in October 1968 (David C Eyre)
Country of origin:
Australia
Description:
Light commercial airliner
Power Plant:
Three 134 kw (180 hp) Lycoming O-360-A1A four-cylinder horizontally-opposed air-cooled engine
Specifications:
- Wingspan: 17.37 m (57 ft)
- Length: 11.12 m (36 ft 6 in)
- Height: 3.32 m (10 ft 9 in)
- Wing area: 30.19 m² (325 sq ft)
- Max speed: 225 km/h (158 mph)
- Cruising speed: 317 km/h (140 mph)
- Initial rate of climb: 317 m/min (1,040 ft/min)
- Absolute ceiling: 6,100 m (20,000 ft)
- Rate of climb at sea level on one engine: 130 m/min (430 ft/min)
- Ceiling one engine out: 2,740 m (9,000 ft)
- Max range with 600 litres (132 Imp gals) of fuel: 1,450 km (900 miles)
- Empty weight: 2,087 kg (4,600 lb)
- Loaded weight: 2,948 kg (6,500 lb)
History:
Following accidents to the Gipsy Major powered de Havilland Drovers in New Guinea, the Australian Department of Civil Aviation (DCA) placed restrictions on the operation of the type, the 11 aircraft then in service being grounded on 11 September 1952 but, after some modifications were made, the grounding was lifted. The restrictions imposed meant that the type was uneconomic for Qantas to operate and that company replaced them with de Havilland DHC-2 Beavers. These accidents, together with the high cost of purchase of the Drover due to the small production run, meant that in the end only 20 aircraft were produced, production ceasing in September 1953.
In 1957, at the request of the New South Wales section of the Royal Flying Doctor Service (RFDS), de Havilland investigated the possibility of installing newer more powerful engines in the Drover, and making other changes to improve performance and payload. The 134 kw (180 hp) Lycoming O-360 engine with a Hartzell constant-speed and feathering propeller was chosen, this unit increasing the power by 40 per cent. The first aircraft modified VH-FDA (c/n 5019) flew in May 1960, and six other Drovers were converted to what became known as the Mk 3 standard.
The first modified aircraft was delivered to the RFDS on 4 June 1960 and in the ambulance role it carried a pilot, two medical staff and two stretchers. It was also decided to modify the tailplane to 13 degrees dihedral for extra stability but only two aircraft, VH-FDA and VH-FDC, were modified. Two further aircraft were subsequently modified, becoming known as the Mk 3A; and one aircraft with the RFDS was permitted to operate at an increased weight of 3,084 kg (6,800 lb), becoming the only Mk 3B. Eventually the Drovers operated by the RFDS at Broken Hill, NSW were replaced by Beagle 206s, which in turn were replaced by the Australian-built GAF Nomad N-22.
In 2020 Drover VH-FBC was restored at Broken Hill, NSW, and placed on display at the RFDSVisitor Centre where it has been repainted as VH-FDA in the green and colour scheme worn by RFDS aircraft in the 1960s.