All Contents
Contents
The Beech 1900 is a 19-passenger and crew of two pressurised airliner based on the Beech 200 Super King Air.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
Initially known as the Raytheon T-6 Texan II, the Texan II is a single-engine turboprop powered advanced trainer produced for the United States Air Force.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
At the conference of the US Regional Airlines Association in 1989 Beech announced it would produce a new variant of the 1900C known as the 1900D.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
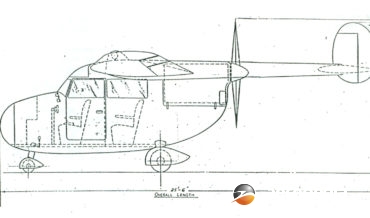
In the 1970s NASA working with Bell and Boeing-Vertol to investigate the tilt-rotor concept for an assault vehicle for the US Army and the result was a twin-engine machine which first flew in 1977, with two prototypes being construction and the type made its first appearance at the 1981 Paris
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
In the 1960s companies such as Soloy looked at re-engining aircraft with turbines and to this end Soloy developed variants of the Cessna 206 and 207, receiving orders in 1964 for 20 Model 206 aircraft.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
Probably one of the most, if not the most, produced helicopters in the world, the Bell 47 series began when the Bell Aircraft Corporation commenced the development of helicopters in 1941 and flew the first of five experimental two-seat prototypes in 1943, the first being known as the Model 30
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Kansan was initially known as the AT-11 and was developed in 1941 from the Beech 18 series for the military navigational training role, a late variant of the Model 18 series being used for this model.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
After the success of the MU-2 series, Mitsubishi decided to proceed further into the world of light executive transports and designed the MU-300 Diamond, two prototypes of which were built, the first flying on 29 August 1978.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
In 1970 the larger Model 58 joined the Beech range, the prototype flying for the first time in June 1969.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The prototype King Air (N5690K), known as the Beech 65-90, was flown for the first time on 20 January 1964.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
Designed to fill the gap between the Beech Baron and the Beech Queen Air in the Beechcraft range, the Model 70 Duke, when it first appeared, was the cheapest fully-pressurised four/six-seat high-performance aircraft with turbocharged engines.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The King Air 300 was a development of the 200 series of corporate aircraft but only 219 examples had been built when production ceased in 1991 in favour of the 300LW.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
Of similar appearance to the Grumman Cougar and Piper Seminole, like those aircraft the Duchess was designed as a low-cost, high-volume, production aircraft featuring honeycomb-bonded wings, handed propellers, and electrically-operated flaps and trim tabs. It was aimed at pilots stepping up from single to twin engined operations, and for those
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The first large twin-engine aircraft built by the Beechcraft Corporation, the Queen Air series of aircraft was introduced to the company’s range in 1958.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Skipper was designed by Beechcraft to meet the needs of aero clubs throughout the world for a light trainer with around 75-kw (100-hp), with good economy of operation, and the capability of using lower octane fuels.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Starship project was revealed to the aviation industry at the NBAA Convention in 1983 shortly after the 85-percent proof-of-concept aircraft was flown at Mojave.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
This was a light aircraft which emanated from the Beaufort Division of the Department of Aircraft Production in October 1945 and, known as the EC-1, was a proposal for the design and production of a four-seat light aircraft using knowledge gained during the production of the Bristol Beaufort bomber during
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The prototype of the Musketeer series of light four-seat monoplanes was flown for the first time on 23 October 1961, and introduced to the Beechcraft range in 1962.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
James R Bede, the well-known light aircraft designed in the USA, formed Bede Aircraft Inc at Newton, Kansas to undertake the design and production of plans and kits of a variety of aircraft for amateur construction.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Beechcraft Debonair was a four-seat, high performance, all-metal low-wing cantilever monoplane with a fully retractable tricycle landing gear.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Bede BD-5 was one of a number of designs produced during the 1960s by Bede Aircraft of Newton, Kansas to meet the requirements of the home constructor.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
Flown of the first time on 22 December 1945, production of the Bonanza, in progressively revised versions, continued for some 42 years this being one of the longest periods of production of any aircraft.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
By late 1971 Bede Aircraft claimed it had 4,300 orders for the BD-5 series but found changes had to be made to the design as flight testing revealed the V-tail was unstable.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The A36 series was a development of the V35 ‘V’-tail series built with a conventional tail unit and with swept-back vertical tail surfaces, an extended cabin, and was first conceived in 1968.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The BD-5 series was the subject over the years of much development due to the difficult constructors were having in locating a suitable engine.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Twin Bonanza was the first twin-engine, light commercial aircraft of post-war design to be produced in the United States.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Bede BD-6 is a single-seat scaled-down development of the popular BD-4 series of light amateur built aircraft designed in the United States. Introduced to the range in 1975 the series is built and marketed by Bedecorp of Medina, Ohio and is of all-metal construction and is supplied in kit
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Beech Baron series was developed by the Beechcraft Corporation as a successor to the Travel Air and Twin Bonanza series.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
Gordon Bedson was born on 23 September 1918 in the Channel Islands and commenced employment with the Miles Aircraft Company in 1936.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Honey Bee was a single-seat all-metal light aircraft designed by William Chana and Kenneth Coward, engineers with Convair in San Diego, in the 1970s. The first example was flown for the first time on 12 July 1952.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Wee Bee was designed in 1924 for the Lympne light aircraft trials by W S Shackleton for William Beardmore & Co Ltd of Dalmuri, Dumbarton Shire, in Scotland.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
Designed by Ted Wells for Walter Beech in 1930, the Model 17 was the first aircraft produced by the newly-formed Beech Aircraft Corp.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Bearhawk Patrol and Bearhawk LSA are developments of the R & B Bearhawk utility aircraft developed in the United States.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The prototype of the Beech 18 series flew for the first time on 15 January 1937.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Bearhawk Patrol is a development of the R & B Bearhawk light utility aircraft which was initially produced in plan form for the amateur aircraft market and is now one of three aircraft in the series which was initially designed by Robert Barrow.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The prototype of the Beechcraft 23 series was flown for the first time on 23 October 1961 and, following certification, deliveries of production machines began during the following year.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Bakeng Duce was designed by Gerald Bakeng in Everett, Washington State in the United States as a high-performance parasol-wing light homebuilt for amateur builders, construction of the prototype being commenced in October 1969 and it was completed six months later.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Eagle was designed as a high-performance low-wing cabin monoplane of wooden construction seating a pilot in front and two passengers side-by-side in the rear and was fitted with a manually-operated outward retractable undercarriage.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
W B (Bill) Barber designed and built a single-seat, all-composite, mid engined light aircraft powered by a Rotax 503 engine.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The BA Swallow was developed by the British Klemm Aeroplane Co Ltd. (later British Aircraft Manufacturing Co.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
Recent Comments
Archives
Categories
- No categories
Categories
- No categories
Latest Posts
Newsletter