All Contents
Contents
This aircraft was registered on 5 March 2013 as VH-NZG³ (c/n 2009-1). It was built by Robert Grigson of Strathfieldsaye, Vic. and is fitted with an Aero Sport Power IO-375-M1B engine driving a Whirlwind Aviation 200RV propeller.
David C. Eyre
- May 25, 2020
This was an ultralight aircraft registered with the RAA as 19-8674 (c/n G27A 82-2-53). Nothing further is known about the design.
David C. Eyre
- May 25, 2020
J Thomas Grant of Dunedin, NZ designed and built and 75% scale replica of a World War I Albatros D.V fighter, build time being in the order of three and a half years.
David C. Eyre
- May 25, 2020
This was an ultralight aircraft built by a number of members of the Gold Coast Ultralight Club at Tallabudgera. At least one example was registered with the RAA on 18 December 1989 as 10-1177 and this aircraft was fitted with a Zenoah G-50 engine.
David C. Eyre
- May 25, 2020
This was an ultralight aircraft known as the Jenner Gippslander Mk 1 and was registered with the RAA on 28 August 1995 and was withdrawn from use on 25 May 2008.
David C. Eyre
- May 25, 2020
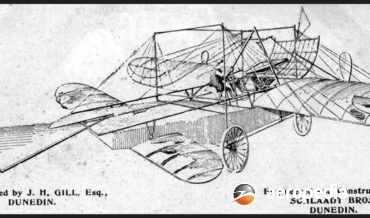
John Harley Gill of Dunedin, NZ, designed and built an aircraft in about 1909, work commencing at about that time in the foundry of Schlaadt Bros in Cumberland Street.
David C. Eyre
- May 25, 2020
This was a light aircraft designed by G A Gerber, the plans of which were released in the magazine Science and Invention in the July 1929 edition.
David C. Eyre
- May 25, 2020
This light aircraft was designed and built by Bryan Gabriel at Holbrook, NSW. It is an approximately 70-percent scale model of a North American P-51D Mustang built of all metal construction and fitted with a converted Mercury six-cylinder Vee outboard engine.
David C. Eyre
- May 25, 2020
The F-14 Tomcat for many years was one of the most potent interceptor / fighters in the armoury of the US Navy and saw combat on a number of occasions operating from aircraft carriers of the US Fleet.
David C. Eyre
- May 25, 2020
Work on an 80% scale all alloy scale replica of the Grumman F-8 Bearcat was commenced in Western Australia in about 2010, the aircraft to be fitted with a new 269-kw (360-hp) Vedeneyev M-14P radial engine driving a four-blade MT propeller.
David C. Eyre
- May 25, 2020
Mr Gavin Grimmer of Hastings, NZ built and flew a Canadian designed Falconar Maranda which in 1995 became ZK-JGR.
David C. Eyre
- May 25, 2020
In 1944 Grumman commenced design of a successor to the successful Goose amphibian and, known as the G-64 Albatross, the first of two prototypes flew on 24 October 1947.
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
In April 1940 the US Bureau of Aeronautics placed a contract with Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation for the construction of two prototypes of a three-seat carrier-borne torpedo bomber known as the XTBF-1.
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
Leroy Grumman was born on 4 January, 1885 in New York and learnt to fly in 1918, becoming a test pilot and engineer at the US Naval Aircraft Factory in 1920.
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
One of the most successful fighter aircraft of World War II, the Hellcat was a development of the Wildcat fitted with a Double Wasp engine providing 1,492 kw (2,000-hp), the prototype, the XF6F-1, flying at Bethpage on 26 June 1942, the second prototype, the XF6F-3 flying six weeks later on
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
The Grebe was designed by H P (Harry) Folland for the Gloster Aircraft Company, this company originating in 1917 as the Gloucestershire Aircraft Company which, at a plant near Cheltenham, established itself by building wooden aeroplanes for the RFC, and later the RAF.
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
The definitive prototype of the Wildcat, known by the manufacturer as the G-36, flew for the first time on 2 September 1937 under the designation XF4F-2.
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
In 1940 the design staff at Gloster Aircraft commenced design of an operational jet fighter to meet specification F.9/40, the aircraft built being the only Allied jet aircraft to see operational service during World War II. On 7 February 1941 the British Ministry of Aircraft Production placed an order for
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
The Grumman G44 Widgeon fours eat light twin-engine, high-wing cabin monoplane amphibian was flown in prototype form for the first time in July 1940.
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
The prototype of the Gloster Meteor fighter was flown for the first time on 5 March 1943. It was the first jet fighter to enter service with the Allies, and thus the type was in service during the closing stages of the conflict against Germany.
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
The Grumman OV-1 Mohawk was developed for the US Army for the observation role, according exceptional visibility to the two man crew and able to carry a variety of cameras, radar and infra-red detection systems for photo-reconnaissance and electronic surveillance.
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
In 1948 Armstrong Whitworth re-designed the Gloster Meteor as a two-seat night fighter and in this regard it fitted the Rolls Royce Derwent 8 in the NF-11 and the Derwent 9 in the NF-12 and NF-14.
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
On 4 December 1952 Grumman Aircraft flew the prototype of what was, for many years, one of the most important anti-submarine aircraft in the western inventory.
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
When the Royal Air force commenced retirement of the Meteor F Mk 4 fighter it looked at converting a number to target drones to help develop ground and air-launched guided missiles and it was decided to convert a number to be used as expendable targets that could be tested to
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
The G.V was one of a series of long-range heavy bombers built by Gothaer Waggonfabrick A G Gotha in Germany which produced the type in some numbers during World War I, the series also being licence built by Luft Verkehrs GmbH (LVG) and Siemens Schuckert Werke GmbH.
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
The Intruder is a twin-engine, two-seat, all-weather strike aircraft tht was built in some numbers for operations from US Navy aircraft carriers and entered service in 1963.
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
The F-16 series was designed as a small, lightweight agile fighter for the US armed services and is one of the most prolific aircraft of its type in the world.
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
On 21 December 1964 the first F-111 flew at Carswell Air Force Base, Texas. It was the product of 25 million man-hours of planning, design, and construction, and 2,100 hours of wind-tunnel testing.
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
The Gauntlet was the last open-cockpit fighter biplane to see service with the RAF, first entering service in May 1935.
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
The Gladiator was the last single-engine biplane fighter built for the RAF and, although obsolescent by the commencement of World War II, it enjoyed some success. Designed by a team lead by H P Folland, it was an extensively refined development of the Gauntlet.
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
The Mirage III emanated from Dassault’s Mirage I, which was powered by two 1,640 lbst Armstrong Siddeley Viper turbojets with provision for a rocket motor in the rear fuselage.
David C. Eyre
- May 19, 2019
The G-550 is one of a series of business and executive jets produced by General Dynamics Gulfstream Aerospace at its facility in Savannah, Georgia marketed under the name V-SP and by early 2016 450 aircraft in the G-550 series had been delivered to a variety of operators for a variety
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
In 2008 Gulfstream announced it was going to introduce a new long-range business aircraft known as the 650 to fill a niche in the corporate market between the company’s own G550 and the Bombardier Global XRS, and the Boeing Business Jet and Airbus Corporate Jetliner.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
In the 1950s the US Navy was seeking a cheap, simple single-seat helicopter for the reconnaissance and assault role, and the Gyrodyne Company of America in St James on Long Island, New York, produced a series of helicopters known as the XRON Rotorcycle between 1954 and 1956.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Speed Canard was designed and developed by Gyroflug-FFT MbH at Menges on the River Danube and placed in small-scale production.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Gyroz two-seat tandem gyrocopter was the culmination of the development of gyrocopters for sports pilots by Advanced Kinetics of Kurrajong, NSW.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
Designed to supplement the two-seat AA-1 Yankee series of aircraft, the AA-5 Traveler series was a four-seat variant which, although similar in appearance to the earlier models, had been extensively re-designed structurally to take the extra load of two more passengers, and the more powerful 112-kw (150-hp) engine.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Cabri is a small, two-seat light helicopter, the production prototype of which (F-WYHG) was flown in March 2005, certification in Europe being obtained in December 2007.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The Grumman G21 series of twin engine amphibians was introduced in 1937.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
The prototype of the Series 1000 (or 695B) was flown for the first time on 12 May 1980 and deliveries of production aircraft began in July of the following year.
David C. Eyre
- May 8, 2019
Recent Comments
Archives
Categories
- No categories
Categories
- No categories
Latest Posts
Newsletter